|
What is it?
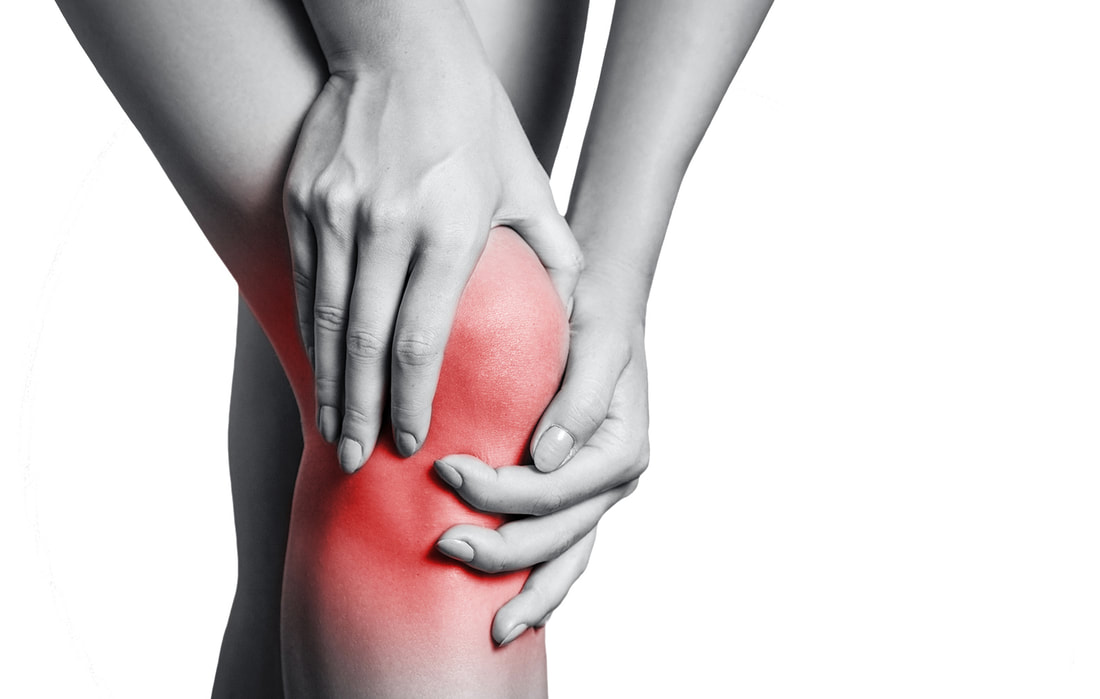
There are two main types of arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis, which is a process by which the body’s own immune system attacks the connective tissue of joints. Osteoarthritis which is essentially wear and tear of the connective tissue of the joints. These two are very different in their presentation and management. Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) is usually something that builds up over time and can become more or less painful with sudden changes to activity. Knee OA usually presents as pain in the knee joint along the joint line, made worse with load bearing activity, particularly twisting and turning. Sometimes this can be accompanied with persistent swelling around the front or back of the knee and stiffness particularly of a morning. What is the cause? There is a small amount of cartilage that sits between the two bones of the knee, femur (thigh) and tibia (shin) This is called the meniscus. This acts as a shock absorber and smooth sliding surface for movement. Over time, this tissue can become scratched and damaged. As the meniscus has very little blood flow it usually doesn’t heal over time and accumulates to reduce the thickness and consistency of the cartilage of the knee. My knee has become painful all of a sudden, Is it getting worse? Knee OA is a progressive degenerative condition, meaning it gets worse slowly over time. Sudden changes to pain levels are usually not attributed to changes in the condition of the knee, rather changes in activity levels, body mass or muscle strength putting greater stress on the existing tissue. Can it be fixed? While the connective tissue of the knee joint itself has a low / slow ability to heal, pain and activity levels can be improved significantly with activity modification, exercise and weight management. Physiotherapy can help prescribe and monitor this program. Reducing body mass will reduce the amount of strain that is placed on the knee joint with each and every step throughout the day, this accumulated reduction in extra strain will help improve the aggravation of the knee joint. Specific exercise to improve strength of the muscles surrounding the knee will improve the body’s ability to adsorb shock through the muscles rather than the joint itself. Do I need to stop walking/ exercising? No. The best way to manage this condition long term is to exercise regularly and consistantly. This will help manage body weight as well as improve strength of the lower limb. Exercise may take other forms like cycling or swimming for a short period of time to reduce loading of the joint temporarily, then building back up to load bearing activity. Do I need to have a knee replacement? In most cases a great deal of gain can be made through managing exercise and body mass. However, if exercise and lifestyle changes fail to see significant improvements to knee pain and function then operative management can be explored. This is a decision that can be made with your GP who will be able to refer to a surgeon. Good gains can be made with lifestyle changes and exercise, this should always be the first port of call. Besides the direct benefits of physio management, lifestyle and exercise modification will also prepaid you for any future operations and lead to a speedier recovery after.
1 Comment
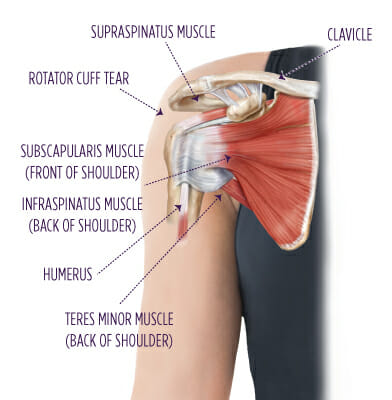
A common finding in the ultrasound of a sore shoulder or hip is ‘Bursal thickening’ or bursitis. So, what does this mean? is it the cause of your pain? and can it be fixed?
What is it? Bursas are small fluid filled sacs which reside throughout joints of the body. Their role is to create a soft, padded, sliding surface between the muscle and bone. Bursitis is when one of these sacks becomes inflamed and swollen. Is it the cause of my pain? Bursal thickening is not a definite cause of pain. Thick bursas are commonly found in non-painful shoulders. A recent study found that 78% of non -painful shoulders had bursal thickening. This is because the thickening of a bursa can be an adaptive mechanism to deal with extra demands. (like getting calluses on your hands) Do I need to get an ultrasound to diagnose it? No, If a bursa is the cause of your pain it will usually be obvious from a physical examination. This could include painful movements, range of motion and timing/pattern of pain. Do I need an injection to heal it? The short answer is no. Although a corticosteroid injection can bring short term relief in some cases. Physiotherapy focusing on a combination of exercise and movement modification can have great long-term results in most cases. What else can be done? If a bursa is becoming inflamed from over-use it may be a matter of reducing certain task, or performing those tasks slightly differently to give the tissue a break. A gradual exercise program will ensure the area remains strong and helps to offload the bursa.
|
Archives
December 2021
Categories |
Proudly powered by Weebly




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed